|
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Free Long Distance
If
you make frequent long distance calls to a remote site, you already
know the charges can add up quickly.
For
Avaya™ Communication Manager environments,
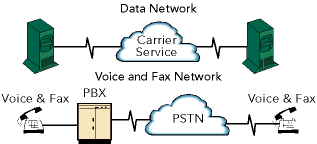
What is VOIP? VOIP lets you make toll-free long distance voice and fax calls over existing IP data networks instead of the public switched telephone network (PSTN). Today businesses that implement their own VOIP solution can dramatically cut long distance costs between two or more locations. That Was Then... For the past 100 years people have relied on the PSTN for voice communication. During a call between two locations, the line is dedicated to the two parties that are using it. No other information can travel over the line, although there is often plenty of bandwidth available. Later, as data communications emerged, companies paid for separate data lines so their computers could share information, while voice and fax communications were still handled by the PSTN.
This Is Now... Today, with the rapid adoption of IP, we now have a far reaching, low-cost transport mechanism that can support both voice and data. A VOIP solution integrates seamlessly into the data network and operates alongside existing PBXs, or other phone equipment, to simply extend voice capabilities to remote locations. The voice traffic essentially ˇ§rides for freeˇ¨ on top of the data network using the IP infrastructure and hardware already in place.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 communications and saves thousands of dollars monthly. Instead of
paying your long distance carrier to route long distance calls between
offices, any IP data network can route the calls using a technology
called Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP) or Internet Telephony.
It doesn't matter if you are using the Internet, a private Intranet,
ISDN, DSL, frame relay, leased line, wireless or satellite for your
data communications network, as long as it uses the Internet Protocol
(IP).
communications and saves thousands of dollars monthly. Instead of
paying your long distance carrier to route long distance calls between
offices, any IP data network can route the calls using a technology
called Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP) or Internet Telephony.
It doesn't matter if you are using the Internet, a private Intranet,
ISDN, DSL, frame relay, leased line, wireless or satellite for your
data communications network, as long as it uses the Internet Protocol
(IP).